Type III Hypersensitivity Reaction
Type III Hypersensitivity, otherwise called insusceptible complex-intervened extreme sensitivity, according to the Lecturio Medical Library happens when antibodies and antigens structure resistant edifices (ICs) available for use and store in vulnerable tissues. The supplement framework triggers the invulnerable reaction, prompting leukocyte enrollment and tissue injury. There is no single clinical condition for this extreme touchiness. Side effects mirror the debilitation of numerous organ frameworks dependent on locales of IC statement. Analytic workup relies to a great extent upon the set of experiences and incorporates research center tests, imaging, and biopsy of the influenced organ. Treatment comprises of expulsion or evasion of culpable specialists and, in serious conditions, glucocorticoids or immunosuppressive treatment.
Outline
Excessive touchiness response
A “hyper” or overstated reaction to what exactly ought to be viewed as innocuous ecological antigens
Types I, II, and III are prompt responses happening inside 24 hours.
Type IV response creates more than a few days.
Type III extreme touchiness response
Invulnerable complex (IC)- interceded extreme touchiness: set off by antigen-immune response (Ag-Ab) edifices stored in tissues
Ag: inherent (part of the host) or extraneous (exogenous source like microbes, infection)
Likewise with type II touchiness, cell injury is comparative: Complement framework prompts a response that produces cell harm.
Not at all like kind II touchiness, in type III responses:
Antigens are not bound to cell surfaces.
Ag-Ab edifices structure available for use.
Focus of the insusceptible reaction isn’t the tissue or cell.
Target is the IC kept in the tissue.
Pathophysiology
Physiology
Safe complex development regularly brings about antigen balance.
The supplement framework decreases pathologic IC aggregation.
Antibodies (Ab) have 2 districts:
Fab district: joins to antigens
Fc district: interfaces with supplement and Fc-bearing receptor (FcR) cells
C1q: enacts supplement framework and ties Ab Fc locale, interceding IC leeway by FcR-bearing cells.
C3b: makes ICs dissolvable and labels them for phagocytosis (opsonization).
Pathogenesis
Insusceptible complex development: IC shaped by the limiting of Ag and Ab
Insusceptible complex testimony
Insusceptible complex testimony relies upon:
Actual properties of the IC:
Proclivity of Ab to supplement, size, and charge of the IC
Expanded pace of IC arrangement → overpowers clearing component → IC uninhibitedly circle out to organs
Antigen-to-immunizer proportion:
Low antibodies or overabundance antibodies → diminished effector initiation
Tissue-explicit hemodynamics
ICs initially confine inside veins → vasculitis
Normal regions influenced are “porousness”- helpless tissues:
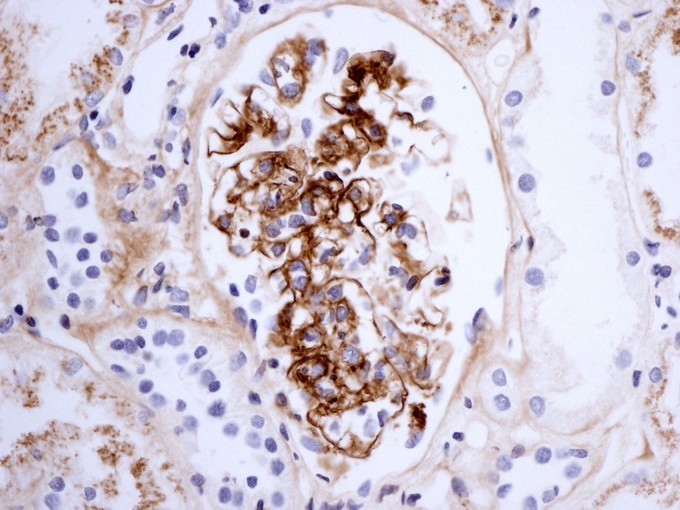
Glomeruli (nephritis)
Joints/synovium (joint inflammation)
Safe complex provocative response
IC stores enact the supplement course.
C3a starts pole cell degranulation:
Histamine increments vascular penetrability in the elaborate tissue.
ICs enter tissue → ordinary tissue with IC turns into an objective for incendiary reaction
C5a (chemoattractant) initiates neutrophils → discharge lysozymes and provocative go betweens → cell passing and tissue injury
C3b opsonizes the tissue → phagocytosis and layer assault complex (MAC)- intervened cell lysis
Macrophages, regular executioner cells → discharge lytic arbiters and harm tissue cells
Platelet conglomeration can happen → miniature clots development
Clinical Presentation
Signs are influenced by the course of passage, site(s) of IC testimony, and perseverance of antigen(s).
Arthus wonder/Arthus response
A privately infused antigen (e.g., inoculation like Tdap) causes a confined response.
Because of antigen overabundance and IC statement on vascular dividers
Putrefaction of influenced tissues: torment, redness, induration, and edema at the site of infusion
Self-restricted
Foundational lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Antibodies coordinated against parts of the core: antinuclear antibodies (ANA), a widespread finding in SLE
Antibodies to different pieces of the core:
Histone (hostile to histone Ab)
DNA (hostile to dsDNA Ab)
Ribonucleoprotein (hostile to RNP Ab)
Extractable atomic antigen/Smith antigen (Anti-Smith Ab)
Other: Antibodies against phospholipids in cells (antiphospholipid Ab)
Present in 30{ec10f60754972d02a9ab0808c273855fb739137b27c4fe172d50938c140bce86}–40{ec10f60754972d02a9ab0808c273855fb739137b27c4fe172d50938c140bce86} of patients with SLE
Expanded danger of apoplexy
Ag-Ab edifices store in various regions:
Skin/mucocutaneous (malar rash, photosensitivity, oral ulcers)
Kidneys (glomerulonephritis)
Joints (joint inflammation)
Veins (vasculitis, Raynaud’s marvel, blood clumps)
Pleura (emanation)
Pericardium (pericarditis)
Platelets (frailty, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia)
Focal sensory system (strokes, seizures)
Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
Response to nephritogenic antigens of gathering A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GAS)
Can be from streptococcal throat contamination or skin disease
Show: hematuria, proteinuria, hypertension, edema, and raised creatinine
Serum affliction
Response to unfamiliar antisera (e.g., counter-agent)
Higher dosages of controlled specialist bound to bring about a response
1 fourteen days after openness: fever, rash, joint inflammation; proteinuria happens with renal inclusion
Extreme touchiness pneumonitis
Extraneous hypersensitive alveolitis
Antigen: a microorganism, protein, or substance
IC statement in alveoli, interstitium, bronchioli, and lung parenchyma
Rancher’s lung: Ag from thermophilic molds on crops
Bird fancier’s infection: Ag from gastrointestinal mucin in droppings or quills
Note: can likewise be T-lymphocyte–intervened (type IV response)
Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN)
Etiology for the most part idiopathic yet can be a response to hepatitis B infection surface Ag
Medium-sized blood vessel aggravation → ↓ blood stream, ↑ apoplexy; saves the veins
Kidneys: most ordinarily elaborate organ
Show:
Delicate erythematous knobs, hypertension, renal inadequacy, and neuropathy
Some have stomach indications (mesenteric arteritis)
Finding and Management
Finding
Clinical history and discoveries (Arthus response, serum affliction regularly analyzed clinically)
Research center tests:
CBC
Paleness, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia: SLE
Eosinophilia: serum affliction, touchiness pneumonitis
Metabolic board
Creatinine is unusual in responses including the kidneys
Serologies and culture
Hepatitis board for polyarteritis nodosa
Culture: streptococcal contamination (just 25{ec10f60754972d02a9ab0808c273855fb739137b27c4fe172d50938c140bce86} of patients will have positive outcomes on the grounds that PSGN happens a long time after the disease)
Supplement levels
By and large found in low levels in related conditions
Antibodies
ANA, against dsDNA Ab, antiSmith Ab, hostile to RNP Ab, antiphospholipid Ab: SLE
PSGN: antistreptolysin O (ASO), streptozyme test
Urinalysis
Proteinuria: SLE, PAN, serum disorder
PSGN: hematuria, proteinuria
Fiery markers
By and large raised C-receptive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) during dynamic irritation
Imaging
High-goal figured tomography (CT) (lung): excessive touchiness pneumonitis
Arteriography or CT/attractive reverberation angiography (MRA): for polyarteritis nodosa
X-beam: joint contribution
Surgeries
Renal biopsy: for renal contribution
Skin biopsy: for cutaneous contribution
Bronchoscopy: for lung contribution
The executives
Eliminate or try not to irritate specialist
Antihistamines, nonsteroidal calming drugs (NSAIDs) for manifestation help (rash, tingling, joint agonies)
In responses because of contamination (PSGN), anti-infection treatment in case disease is as yet present
Control of entanglements like hypertension (PSGN, PAN), edema (PSGN, SLE), aviation route indications (extreme touchiness pneumonitis)
Glucocorticoids utilized in extreme cases to smother aggravation
Restorative choices for explicit conditions:
Excessive touchiness pneumonitis: immunosuppressive treatment (mycophenolate, azathioprine)
SLE:
Antimalarials (hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine)
Immunosuppressive treatment: mycophenolate, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, rituximab
Long haul anticoagulation if with apoplexy: warfarin, low-atomic weight heparin
Dish:
Methotrexate, an infection adjusting against rheumatic medication (DMARD)
Immunosuppressive treatment (cyclophosphamide, azathioprine)
Dialysis for end-stage renal illness from SLE
Organ transplantation:
Lung transplantation for cutting edge lung illness in excessive touchiness pneumonitis
Renal transplantation for end-stage renal illness in SLE